Using Supercomputers to Estimate the Radio Propagation Characteristics
Using Supercomputers to Estimate the Radio Propagation Characteristics
Using Supercomputers to Estimate the Radio Propagation Characteristics of Aircraft Cabin and Bullet Trains
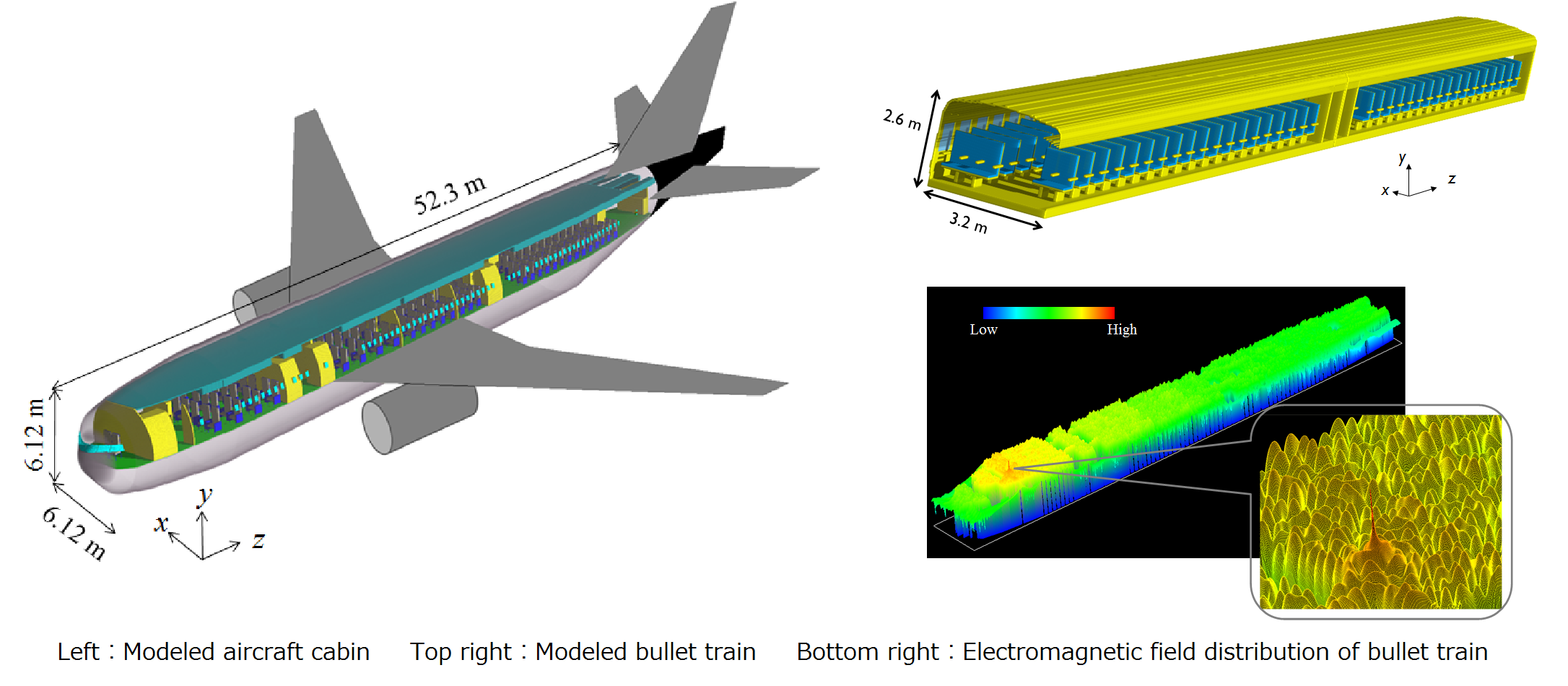
One attractive approach to reducing operating costs of aircraft is to replace the traditional wire harness with wireless links to power systems such as emergency lights or atmospheric pressure sensors. Radio link design must consider propagation characteristics in realizing highly reliable wireless communication. It is known that the electromagnetic field distribution within aircraft cabin is complex because the tight metal surroundings create multiple reflections. To accurately evaluate propagation characteristics of such an environment, supercomputer simulations are suitable.
Numerical estimation of radio propagation characteristics for 5th generation communication system using super computer and high resolution modeling
Many studies are being conducted both domestically and abroad to realize 5th generation mobile and wireless communication (5G) as the next generation communication system. 5G is intended to achieve 'Higher data rates' and 'Reduced latency' matching that of the wired network and 'Higher system capacity' in sensor network etc. It is attracting attention as the basic technology of the Internet of things (IoT). 5G is expected to use a higher frequency band (6 GHz or higher) than that used by the 4th generation mobile and wireless communication systems. In order to design a radio circuit that realizes reliable and high-quality communication, it is necessary to comprehensively evaluate the factors that are important in radio wave propagation characteristics, such as human body shielding as well as considering the reflection characteristics due to wall surface roughness, and their influence of system performance.
